|
Keynotes Speaker |
|
 |
M. Jamal Deen McMaster University, Canada Title: |
ABSTRACT: The convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and smart sensor technologies is revolutionizing healthcare by enabling real-time monitoring, personalized health interventions, and ambient assisted living. In this talk, I will present a comprehensive overview of AI-enabled smart systems across the domains of mobility analysis, smart medical homes, wearable telehealth platforms, and lifestyle management tools. I will then discuss a holistic view of a smart medical home ecosystem driven by sensor fusion, edge computing, and AI analytics that form the core of next-generation aging-in-place and daily activity monitoring. Central to this is the concept of a "brain" or and autonomic decision-making system that orchestrates data flow, interprets contextual information, and delivers intelligent outputs. A key focus of the talk will be our mobility and walking pattern analyzer, a multi-sensor AI-based system that assesses gait and mobility patterns in real-time, empowering early gait diagnostics and rehabilitation tracking. I will also introduce the smart living diary, a multi-modal interface aggregating activity, nutrition, and sleep data to promote healthy lifestyle. Next, I will highlight the growing role of wearable telehealth devices and how AI augments their predictive and diagnostic capabilities. Trends in ubiquitous healthcare and sensor performance will be discussed, alongside ethical and interoperability challenges. The presentation will conclude with a forward-looking perspective on the future of AI-enabled healthcare, emphasizing the need for standardized frameworks, inclusive design, robust privacy-preserving mechanisms and future pathways for research and implementation in smart healthcare systems.
BIO:
Dr. M. Jamal Deen is Distinguished University Professor and Director of the Micro- and Nano-Systems Laboratory at McMaster University. His current research interests are nanoelectronics, optoelectronics, nanotechnology, data analytics and their emerging applications to health and environmental sciences. As an educator, he won the Ham Education Medal from IEEE Canada, the McMaster University President’s Award for Excellence in Graduate Supervision, and the MSU Macademics’ Lifetime Achievement Award (highest award at McMaster University voted by the students) for his exceptional dedication to teaching and significant contribution to student life, academia, and the community at large. Recently (2024), he was the inaugural winner of the SM Sze Education Award from the IEEE Electron Devices Society “For impact leadership and global dissemination of biosensor education in underprivileged regions.”
As an undergraduate student at the University of Guyana, Dr. Deen was the top ranked mathematics and physics student and the second ranked student at the university, winning the Chancellor’s gold medal and the Irving Adler prize. As a graduate student, he was a Fulbright-Laspau Scholar and an American Vacuum Society Scholar. His awards and honors include the Callinan Award as well as the Electronics and Photonics Award from the Electrochemical Society; a Humboldt Research Award from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation; the Eadie Medal from the Royal Society of Canada; and the McNaughton Gold Medal, the Fessenden Medal and the Gotlieb Computer Medal, all from IEEE Canada. In addition, he was awarded the five honorary doctorate degrees in recognition of his exceptional research, scholarly and education accomplishments, exemplary professionalism and valued services.
Dr. Deen has been elected by his peers as Fellow/Academician of thirteen national academies and professional societies including The Royal Society of Canada - The Academies of Arts, Humanities and Sciences (the highest honor for academics, scholars and artists in Canada), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (China’s highest national honor in the area of science and technology and highest academic title), , the National Academy of Sciences India, the Canadian Academy of Engineering, IEEE, APS (American Physical Society) and ECS (Electrochemical Society). He served as the elected President of the Academy of Science, The Royal Society of Canada in 2015-2017. Recently, he was elected the inaugural Vice President (North) of The World Academy of Sciences, representing the developed countries. He was also elected to the Order of Canada, the highest civilian honor awarded by the Government of Canada.
 |
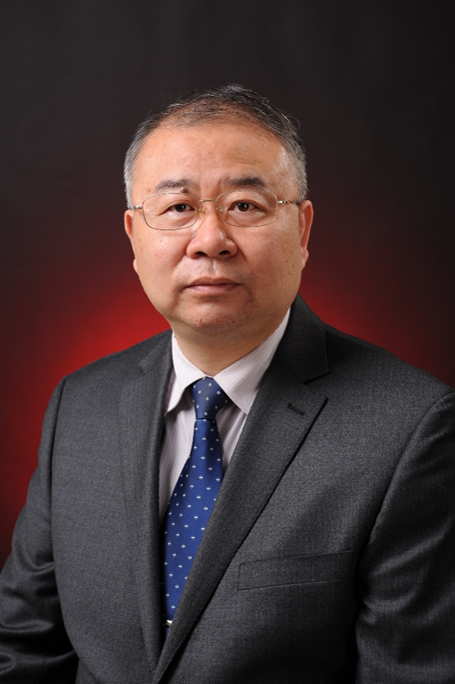
Anders Lindquist Anhui University, China Title: |
ABSTRACT: We are now in the 4th industrial revolution, based on cyber-physical systems that integrate computational algorithms and physical components seamlessly. Cyber-physical systems combine the theories of communication, computation, and control, which were developed by scientists who were both mathematicians and engineers. Mathematics has thus become crucial for technological progress and is essential for a knowledge-based economy. This talk demonstrates, through examples, the role of mathematical sciences in industrial innovation and shows how mathematics enables technology transfer.
BIO: Anders Lindquist received his Ph.D. from KTH Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden, in 1972, an honorary doctorate from Technion (Israel Institute of Technology) in 2010, and a doctorate jubilaris from KTH in 2022. He is currently Distinguished Professor at Anhui University, Chair Professor Emeritus at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Professor Emeritus at KTH. He previously had a full academic career in the United States and was appointed to the Chair of Optimization and Systems at KTH in 1983. He is a Member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Engineering Sciences, a Foreign Member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, a Foreign Member of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences, a Member of Academia Europaea (Academy of Europe), and a Member of the National Academy of Artificial Intelligence. He is a Life Fellow of IEEE, and a Fellow of SIAM and IFAC. He received the 2009 Reid Prize in Mathematics from SIAM and the 2020 IEEE Control Systems Award, the IEEE field award in Systems and Control.
 |
Xingwei Wang Northeastern University, China Title: |
ABSTRACT: With the increasing complexity and decentralization of network environments, traditional network architectures encounter critical challenges, including limited scalability, inadequate intelligence, and insufficient trust assurance. In this context, enabling distributed self-learning, self-adaptation, and self-adjusting under privacy-preserving constraints has become essential for enhancing network performance. To address these issues, we propose a distributed and trustworthy knowledge-defined networking architecture. This framework integrates knowledge-defined networking, federated learning, and blockchain technologies to support distributed modeling and trust mechanisms, thereby advancing the intelligent evolution of networks. Its core contribution lies in overcoming the rigid control paradigms of traditional architectures, fostering a flexible and scalable collaborative ecosystem, and providing efficient and trustworthy infrastructure support. Ultimately, it establishes both theoretical and technical foundations for sustainable next-generation network architectures.
BIO:
Xingwei Wang, Ph.D., is Vice President, Professor, and Ph.D. Supervisor at Northeastern University, China. He is a recipient of the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars, an expert with the State Council Special Government Allowance, and a Fellow of both the China Computer Federation and the China Communications Society.
Professor Wang has received numerous national and provincial awards, including the State Scientific and Technological Progress Award and the National Teaching Achievement Award. He has published over 100 papers in top international journals such as IEEE Transactions and leading conferences including ACM SIGCOMM, with more than 300 SCI-indexed publications. He has also authored 9 academic monographs and holds 66 national invention patents. His research interests include the Internet, cloud computing, and cyberspace security.
 |
Hikmet Sari Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, China Title: |
ABSTRACT: Over the past three decades, wireless communications have evolved from 1G to 5G, and research currently is now focused on 6G. The fi rst generation (1G) was analog, and 2G, predominantly based on GSM, was actually the first generation of digital cellular. These two generations were basically for telephony services. Next came 3G with low- to moderate-speed data allowing mobile Internet. This generation was followed by 4G, which enabled communication between devices, opening the way to machine-type communications, and Internet of Things (IoT). The following generation (5G) had the goal of providing enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB), more efficient machine-type communications (MTC), and Ultra-Reliable and Low Latency Communications (URLLC). Looking now into the future, 6G networks are envisioned to create an intelligent and multi-functional digital ecosystem with sensing, localization, control, and computing, in addition to communication. They are intended to fulfill current industry and consumer demands of high throughput, massive connectivity, semantic communication, ubiquitous wireless environment, low power, and low latency. 6G systems must fulfill much more stringent requirements than 5G systems on transmission capacity, reliability, latency, coverage, and connection density in order to bring a variety of disruptive new applications like Tactile Internet and Holographic Communications. In this talk, we review the evolution of multiple access over 5 generations of wireless communications and comment on recent work for future 6G networks.
BIO:
Hikmet Sari is a Professor at Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing, China. From 2003 to 2016, he was Professor and Department Head at Supelec, near Paris, and Chief Scientist of Sequans Communications. Prior to this, he held various research and managerial positions
in industry including Philips, SAGEM, Alcatel, Pacifi c Broadband Communications,
and Juniper Networks. He holds an Engineering Diploma and a Ph.D. from the ENST, Paris, France. He was elevated to the IEEE Fellow Grade in 1995 for his contributions during the 1980s to advanced signal processing for digital microwave radio systems, but he is best known today for his pioneering work in the 1990s on OFDM, OFDMA, and Single-Carrier Transmission with Frequency-
Domain Equalization (SC-FDE), which signifi cantly infl uenced the IEEE 802.16e and
the 3GPP LTE standards. He also published the first papers on Non-Orthogonal Multiple Access (NOMA) back in the year 2000. His distinctions include election to the IEEE Fellow Grade (1995), the Andre Blondel Medal (1995), the Edwin H. Armstrong Achievement Award (2003), the Harold Sobol Award (2012), election to
the European Academy (2012), election to the Science Academy of Turkey (2012),
and the Heinrich Hertz Award (2021).
 |
Mohsen Guizani University of Artificial Intelligence, UAE Title: |
ABSTRACT: The exponential growth of IoT devices in AI/ML applications has created new opportunities and challenges. To meet the diverse requirements of intelligent autonomous IoT systems while ensuring privacy, Federated Learning (FL) and Multi-agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) have been effectively utilized. IoT systems leveraging edge computing, security technologies, and machine learning can enable smart autonomous systems. FL provides a platform to protect data and reduce latency in these applications. However, resource-constrained IoT devices introduce challenges for computation and communication efficiency. This talk presents research efforts addressing these challenges and explores solutions using FL and MARL in smart city environments.
BIO:
Mohsen Guizani (Fellow, IEEE) received the BS (with distinction), MS, and PhD degrees in Electrical and Computer Engineering from Syracuse University, USA. He is currently a Professor of Machine Learning at the Mohamed Bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI), Abu Dhabi, UAE. Previously, he held positions at multiple institutions in the USA. His research interests include applied machine learning and AI, smart cities, IoT, intelligent autonomous systems, and cybersecurity.
Dr. Guizani became an IEEE Fellow in 2009 and was listed as a Clarivate Analytics Highly Cited Researcher in Computer Science from 2019 to 2022. He has received numerous awards, including the 2015 IEEE Communications Society Best Survey Paper Award, the 2021 Best ComSoc Journal Paper Award, and five Best Paper Awards from ICC and Globecom Conferences. He is the author of 11 books, over 1000 publications, and several US patents. He has also received the 2017 IEEE ComSoc Wireless Technical Committee Recognition Award, the 2018 AdHoc Technical Committee Recognition Award, and the 2019 IEEE Communications and Information Security Technical Committee Award.
Dr. Guizani served as Editor-in-Chief of IEEE Network and currently serves on the editorial boards of multiple IEEE journals and magazines. He has chaired the IEEE ComSoc Wireless Technical Committee and the TAOS Technical Committee, and has served as an IEEE Computer Society Distinguished Speaker. He is currently an IEEE ComSoc Distinguished Lecturer.
 |
Geyong Min The University of Exeter, UK Title: |
ABSTRACT: As intelligent applications continue to proliferate, edge computing has emerged as a cornerstone of modern digital infrastructure. However, the distributed and heterogeneous nature of edge resources poses several key challenges, including high deployment costs, significant resource fragmentation, and underutilized system capacity. To address these challenges and achieve scalable and adaptive edge intelligence, this talk explores a holistic approach through three interrelated strategies: 1) a cooperative edge server deployment framework; 2) a hybrid architecture integrating both static and dynamic edge servers; and 3) a task-aware, fine-grained service placement mechanism. Emerging future research directions will also be discussed. Together, these solutions provide a forward-looking blueprint for building intelligent, adaptive, and cost-effective edge infrastructures capable of supporting the next generation of AI-driven services.
BIO: Professor Geyong Min‘s research interests include Computer Networks, Cloud and Edge Computing, Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing, Systems Modelling, and Performance Engineering. His research has been supported by European Horizon-2020, UK EPSRC, the Royal Society, the Royal Academy of Engineering, and industrial partners. He has published over 200 research papers in leading international journals, including IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Transactions on Computers, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, and IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, as well as in major conferences such as SIGCOMM-IMC, INFOCOM, and ICDCS. He serves as an Associate Editor for several international journals, including IEEE Transactions on Computers and IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, and has held General Chair and Program Chair roles for multiple international conferences in Information and Communications Technologies.
Organizers:




IEEE Ethics Reporting
IEEE Privacy Policy
Copyright AI for Science - 2025. Created and Maintained by AI for Science - 2025 Web Team.